STPM Semester 1 Chemistry Experiment 1 : Volumetric Analysis - Stoiciometry
Here are the answers to the experiment.
Report
Day :
Date :
Topic : Volumetric Analysis - Stoichiometry
Purpose : To determine the exact concentration of a monobasic acid, HX
Apparatus : 250 cm3 volumetric analysis with stopper, 25.0 cm3 pipette, 50.00 cm3 burette, retort stand with clamp, filter funnel, glass rod, pipette pump, electronic balance, conical flask, 50 cm3 beaker, dropper, spatula, 250 cm3 beaker
Materials : Phenolphthalein as indicator, distilled water, solid sodium hydroxide, NaOH, monobasic acid, HX
Theory introduction : Neutralisation occur when an acid react with base. In laboratory, the concentration of an unknown acid can be determined using titration technique. Therefore, this experiment is conducted to determine the unknown acid concentration.
Procedure :
Part A
Part A
- A spatula was used to transfer solid sodium hydroxide, NaOH, into a 50cm3 beaker placed on a electronic balance. 5.02 g* of solid sodium hydroxide, NaOH was weighed.
- Distilled water was added into the beaker containing the solid sodium hydroxide, NaOH. The solid was then stirred by using a glass rod until it was completely dissolved.
- The sodium hydroxide solution was then transferred into the 250cm3 volumetric flask througha filter funnel.
- Distilled water was added into the volumetric flask until the level was within about few centimetres below the calibration mark. A dropper was used to add in the distilled water into the volumetric flask, drop by drop, until it reaches the calibration mark.
- The volumetric flask was shaken and inverted to make sure the solution mix well and a homogenous 0.502 mol dm-3 * sodium hydroxide, NaOH solution was obtained.
Part B
- 100 cm3 of monobasic acid, HX and 100 cm3 of sodium hydroxide, NaOH solution was poured into two separate beakers.
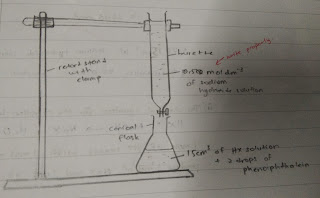
- 25.0 cm3 of the monobasic acid, HX was the pipetted into a clean conical flask. By using a clean dropper, two drops of phenolphthalein were added into the conical flask containing the monobasic acid, HX as an indicator.
- The burette was filled with the prepared sodium hydroxide solution and the initial reading was recorded.
- The apparatus was set up as shown in the diagram. The burette was clamped to a retort stand.
- The sodium hydroxide solution was then added into the conical flask containing monobasic acid, HX, from the burette, until a hint of a very fade pink starts to appear. Then, the sodium hydroxide solution was added drop by drop until the solution in the conical flask changed from colourless to light pink. Make sure to swirl the conical flask during this particular step to make sure the solution is evenly mixed.
- Final burette reading was recorded.
- Step 1 to 7 in part B was repeated twice to obtain a total of sets of data.
- The data was recorded and tabulated. Calculation was made to determine the average titre value and the exact concentration of monobasic acid, HX solution was provided.
Diagram :
Result :
Conclusion : The exact concentration of a monobasic acid is 0.525 mol dm-3






Comments
Post a Comment
Respect others. And you will be respected.